Satanic rituals have long been a subject of fascination, fear, and misunderstanding. Often portrayed sensationalistically in media, these rituals have captured the imagination of many, contributing to an aura of mystery and misconception. In this article, we will delve into the origins, practices, and symbolism of Satanic rituals to shed light on their true nature, separating fact from fiction.
Understanding Satanic Rituals
Satanic rituals are ceremonial practices associated with certain belief systems that revere or invoke Satan, often depicted as a symbol of rebellion, opposition, or an embodiment of evil. It is important to note that there are different groups and subcultures that identify with Satanism, each with its own unique beliefs and practices.
While the term “satanic ritual” may conjure up images of sinister activities, it is crucial to approach the topic with an open mind and discernment. Not all rituals associated with satanic belief systems involve illegal or harmful actions. Many adherents see these rituals as a means of self-expression, personal empowerment, or as a symbolic representation of their philosophical beliefs.
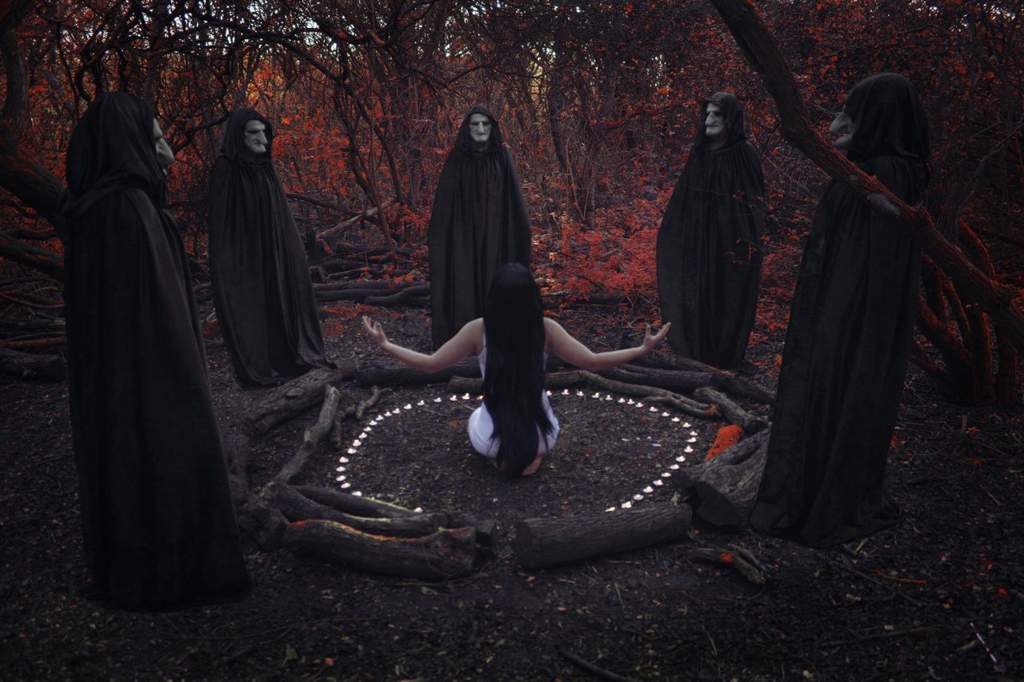

Historical Origins of Satanic Rituals
The historical origins of Satanic signs are complex and multifaceted, drawing from a diverse range of cultural, religious, and philosophical sources over centuries. It’s important to note that the term “Satanic rituals” has been used to describe a wide variety of practices, often with different meanings and intentions depending on the historical context and cultural milieu. Here are some key aspects to consider when exploring the historical origins of Satanic rituals:
- Ancient Mythologies and Religious Contexts: The concept of a rebellious figure opposing divine or cosmic forces has roots in various ancient mythologies and religious texts. In ancient Hebrew texts, the term “satan” originally referred to an adversary or accuser, rather than the malevolent figure commonly associated with Satanism today. Ancient religions often included deities or spirits representing chaos, primal forces, or nonconformity, which could be interpreted as precursors to the figure of Satan.
- Medieval Witch Trials and Occultism: During the European witch trials of the Middle Ages and Early Modern period, accusations of Satanic rituals and witchcraft were rampant. These trials, driven by religious and societal fears, led to the persecution and execution of numerous individuals. Many of the rituals attributed to witches during this time were likely fabrications, reflecting societal anxieties rather than accurate depictions of practices.
- Renaissance and Occult Revival: The Renaissance saw a resurgence of interest in occultism, alchemy, and esoteric knowledge. Figures like Johann Weyer and Johannes Trithemius explored demonology and magic, contributing to the evolving concept of Satanic practices. Grimoires (books of magic) emerged during this period, containing rituals and invocations that were often attributed to demons or infernal spirits.
- 19th and 20th Century Occult Movements: The 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed the emergence of occult and magical organizations that incorporated Satanic themes into their practices. Figures like Aleister Crowley, who founded the religion of Thelema, incorporated elements of rebellion, individualism, and ritual into their teachings. The concept of Satan was often reinterpreted as a symbol of personal liberation and defiance against conventional morality.
- Modern Satanic Organizations: The mid-20th century saw the establishment of organized Satanic groups, such as the Church of Satan founded by Anton LaVey in 1966. LaVey’s “Satanic Bible” outlined a philosophy centered on self-indulgence, individualism, and ritual as psychological tools. These rituals often emphasize self-discovery, catharsis, and empowerment, challenging traditional religious and moral values.
- Contemporary Interpretations: In recent decades, groups like The Satanic Temple have emerged, advocating for secularism, social activism, and the separation of church and state. These organizations use Satanic imagery and rituals as a means of challenging religious privilege and promoting social justice causes.
In summary, the historical origins of Satanic rituals are rooted in a complex interplay of cultural, religious, and philosophical influences. These rituals have evolved over time, reflecting shifting societal attitudes toward individualism, rebellion, and the search for personal meaning
Religious Perspectives on Satanic Rituals
Religious perspectives on Satanic rituals vary widely and are often influenced by the specific beliefs, traditions, and cultural contexts of different faiths. Here, we’ll explore how various religious perspectives view Satanic rituals:
A. Christianity
In Christianity, Satanic rituals are generally viewed as practices that oppose and defy the teachings of Christianity. Satan is considered the embodiment of evil and evil symbols, and rituals associated with Satan are seen as acts of rebellion against God. Many Christians believe that engaging in Satanic rituals can lead individuals down a path of spiritual and moral corruption. The concept of Satanic rituals has also been linked historically to accusations of witchcraft and demonic possession.
B. Islam
Islam holds a similar perspective to Christianity when it comes to Satanic rituals. The Qur’an emphasizes the existence of Satan (known as Shaytan) as a deceiver and tempter. Engaging in practices associated with Satan is strongly discouraged, as they are considered a deviation from the path of righteousness prescribed by Islam. In Islamic theology, believers are encouraged to seek refuge in God and resist the allure of Satanic influences.
C. Judaism
Within Judaism, the concept of Satan has evolved over time. While Satan is not as prominent a figure in Judaism as in Christianity or Islam, some Jewish traditions acknowledge the existence of a “satanic” force that tests individuals’ commitment to God. Engaging in rituals associated with Satan would be seen as a departure from the worship of the one true God. Jewish perspectives on Satanic rituals vary among different sects and interpretations.
D. Neopagan and Occult Traditions
Some neopagan and occult traditions incorporate elements of Satanic symbolism or themes, often interpreting Satan as a symbol of rebellion, personal empowerment, or the primal forces of nature. These perspectives may utilize Satanic imagery and rituals to explore personal growth, self-discovery, and a connection with the natural world. It’s important to note that these interpretations differ significantly from the conventional understanding of Satan in mainstream Abrahamic religions.
E. Satanic and LHP Beliefs
Within modern Satanic and Left-Hand Path (LHP) belief systems, Satanic rituals are central to their practices. These groups, such as the Church of Satan and The Satanic Temple, often embrace Satan as a symbol of individualism, critical thinking, and personal autonomy. Satanic rituals within these contexts are often designed for psychological empowerment, self-expression, and challenging societal norms. Practitioners emphasize that their rituals are not about worshiping a literal Satan, but rather about embracing their own values and identities.
F. Secular Perspectives
Some individuals and organizations approach Satanic rituals from a secular standpoint, using symbolism and rituals to express their skepticism of religious authority, promote secularism, and advocate for social justice issues. The focus is on using Satanic imagery as a means of political and cultural commentary rather than engaging in traditional religious practices.
In conclusion, religious perspectives on Satanic rituals are highly diverse, ranging from strong condemnation within mainstream Abrahamic religions to symbolic and ritualistic interpretations within neopagan, occult, and Satanic belief systems. These perspectives reflect the broader spectrum of religious beliefs and attitudes toward spirituality, morality, and the human experience.

Common Satanic Rituals
Satanic rituals can vary widely in form, intent, and practice, depending on the specific belief system or organization involved. It’s important to note that not all Satanic rituals involve malevolent or nefarious actions; many are focused on personal growth, empowerment, or philosophical exploration. Here are a few examples of Satanic rituals and how they might be performed:
- Empowerment Ritual: This type of ritual aims to empower participants by embracing their inner desires and strengths. It might involve creating a sacred space with candles, incense, and ritual tools. Participants may recite affirmations or invocations that emphasize personal autonomy, self-confidence, and the pursuit of individual goals. The ritual might culminate in a symbolic act, such as breaking a barrier or making a declaration of personal intent, to signify breaking free from societal constraints.
- Ritual of Self-Discovery: In this type of ritual, individuals engage in introspection and self-exploration. Participants might meditate on aspects of themselves they wish to understand better, confront fears or insecurities, and embrace their “shadow” selves—the hidden or suppressed aspects of their psyche. The ritual may involve visualization exercises, journaling, or even creating art to express inner thoughts and emotions.
- Symbolic Invocations: Some Satanic rituals involve invoking symbolic entities or archetypes, rather than literal demons or deities. Participants might use sigils, words, or gestures to connect with aspects of themselves or universal concepts they wish to embody. These invocations can serve as tools for introspection and personal transformation, allowing individuals to tap into different facets of their psyche.
- Community Gatherings: Many Satanic organizations hold communal rituals as part of their activities. These gatherings may include discussions of philosophical principles, sharing personal experiences, and participating in group rituals. The rituals can be designed to foster a sense of camaraderie, solidarity, and shared identity among members who share similar beliefs and values.
- Social Activism Rituals: Certain Satanic groups, like The Satanic Temple, use rituals to promote social and political causes. These rituals might involve symbolic actions or performances aimed at challenging religious privilege, advocating for the separation of church and state, or addressing social justice issues. The focus is often on using Satanic symbolism as a means of raising awareness and provoking thought.
It’s important to emphasize that the examples above are not exhaustive, and Satanic rituals can encompass a wide range of practices and intentions. The rituals are often personalized to align with an individual’s or group’s specific beliefs and goals.
Potential Risks of Satanic Rituals
Before engaging in Satanic rituals, individuals should be aware of potential risks and exercise caution. While many Satanic rituals focus on personal empowerment, self-expression, and psychological exploration, there are important factors to consider to ensure a safe and responsible approach:
- Mental and Emotional Preparedness: Satanic rituals often involve introspection and may bring up intense emotions or thoughts. Participants should be mentally and emotionally prepared to confront and process these experiences. If someone is dealing with trauma, mental health issues, or emotional vulnerabilities, they should exercise caution or seek professional guidance before engaging in such rituals.
- Symbolism and Intent: Understand the symbolism and intent behind the ritual you are considering. Be clear about why you are performing the ritual and what you hope to achieve. This clarity will help you stay focused on your goals and avoid unintended consequences.
- Research and Understanding: Educate yourself about the specific ritual you plan to perform. Understand the historical, cultural, and philosophical context behind it. Misinterpretation or incomplete knowledge could lead to misunderstanding or unintentional outcomes.
- Physical Safety: Ensure that the ritual environment is safe and free from potential hazards. If candles or incense are used, take precautions to prevent fires. Also, be mindful of any physical limitations or health concerns that might affect your ability to engage in ritual activities.
- Personal Boundaries: Set clear personal boundaries before participating in a ritual. Know your limits and be prepared to stop or modify the ritual if you feel uncomfortable or unsafe at any point.
- Group Dynamics: If participating in a group ritual, consider the dynamics of the group and the intentions of the other participants. Be wary of any group or leader that pressures you to engage in activities that go against your values or comfort level.
- Legal and Social Implications: Depending on your location and the nature of the ritual, there might be legal or social consequences to consider. Make sure you are aware of any legal restrictions on certain activities or public displays that could lead to misunderstandings or legal issues.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Be respectful of cultural and religious sensitivities, especially if your ritual involves symbols or practices that might be offensive or misinterpreted by others.
- Intent and Responsibility: Understand that the intent of most Satanic rituals is personal growth and empowerment, not malevolent actions. However, be aware that some practices may be perceived negatively by others, and take responsibility for the potential impact your actions might have on your own well-being and relationships.
- Professional Guidance: If you have concerns or uncertainties about performing Satanic rituals, consider seeking guidance from mental health professionals, religious advisors, or experts in the specific belief system you are exploring.
Remember, responsible and informed participation in any ritual is crucial. Always prioritize your well-being, safety, and personal values when deciding whether to engage in any form of ritual practice.
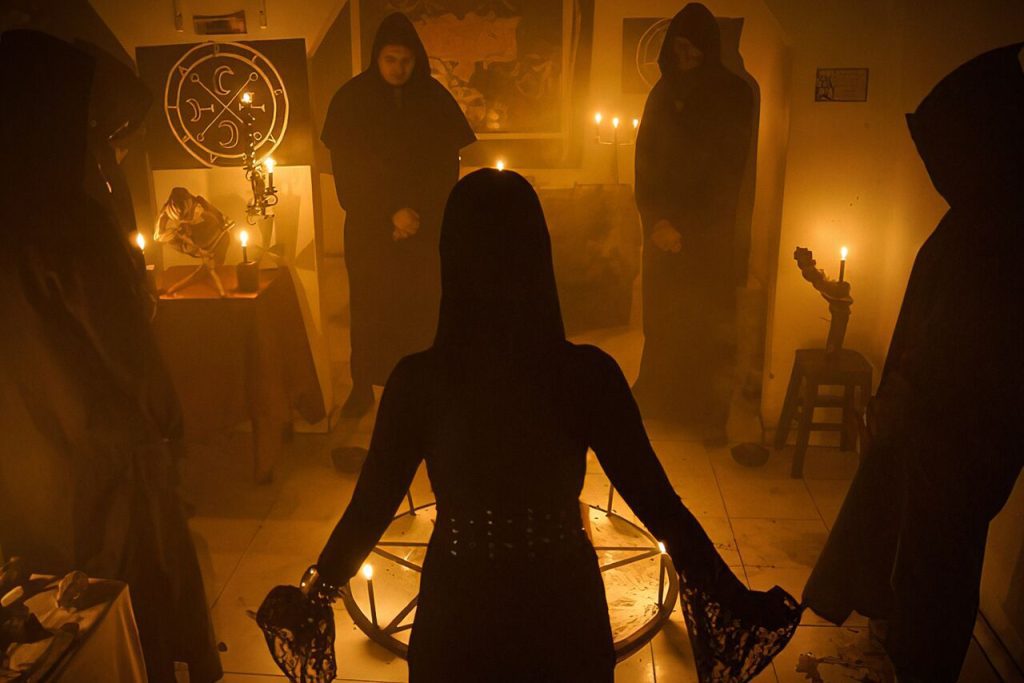
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations play a significant role in any aspect of life, including religious and spiritual practices like Satanic rituals. When engaging in such rituals, it’s important to be mindful of ethical principles to ensure that one’s actions align with personal values, respect for others, and the well-being of oneself and the community. Here are some ethical considerations to keep in mind when it comes to Satanic rituals:
- Respect for Autonomy: Individuals should have the autonomy to decide whether to engage in Satanic rituals based on their own beliefs and values. No one should be coerced or pressured into participating against their will.
- Informed Consent: If participating in group rituals, ensure that all participants have a clear understanding of the purpose, symbolism, and potential outcomes of the ritual. Informed consent allows individuals to make informed decisions about their involvement.
- Safety and Well-Being: Prioritize the physical, mental, and emotional well-being of participants. Rituals should not pose a risk to physical safety or mental health. Anyone who feels uncomfortable or unsafe should have the freedom to disengage from the ritual.
- Intention and Consequences: Consider the intentions behind the ritual and the potential consequences of your actions. Ethical rituals should align with positive values, personal growth, and respectful interaction with others.
- Legal and Social Boundaries: Stay within legal and social boundaries when performing satanic rituals. Avoid engaging in activities that could lead to legal trouble or harm your reputation within your community.
- Transparency and Honesty: Be open and honest about your beliefs and practices, especially if they involve Satanic symbolism. Misrepresenting your intentions or affiliations could lead to misunderstandings or conflicts.
- Intent vs. Harm: Evaluate whether your actions have the potential to cause harm to yourself, others, or the environment. Strive to ensure that your intentions align with positive outcomes and personal growth.
- Responsibility: Take responsibility for your own actions and their potential impact. Reflect on the ethical implications of your choices and be willing to address any unintended consequences that arise.
Ultimately, ethical considerations are about thoughtful reflection, responsible decision-making, and a commitment to personal and communal well-being. By approaching Satanic rituals with an ethical mindset, individuals can engage in meaningful practices that foster personal growth, empowerment, and respect for themselves and others.
Helpful Resources For Satanic Rituals
If you’re interested in learning more about Satanic rituals, philosophy, and practices, there are various resources available that can provide insights and guidance. It’s important to approach these resources with an open mind and critical thinking, considering the diversity of perspectives within the realm of Satanic belief systems. Here are some helpful resources:
- Books: “The Satanic Bible” by Anton LaVey: This foundational work outlines the philosophy and rituals of the Church of Satan, offering insights into LaVey’s Satanic ideology. “The Satanic Rituals” by Anton LaVey: A companion to “The Satanic Bible,” this book delves into specific ritual practices and their symbolic meanings.
- Websites and Organizations: The Church of Satan: The official website of the Church of Satan provides information about their philosophy, rituals, and activities. The Satanic Temple: The Satanic Temple is a non-theistic religious organization that uses Satanic symbolism for political and social activism. Their website offers resources and insights into their beliefs and actions.
- Documentaries and Media: Documentaries such as “Hail Satan?” provide an in-depth look at the Satanic Temple’s activism and philosophy. Podcasts and YouTube channels hosted by practitioners or scholars in the field can offer insights into different perspectives on Satanic rituals.
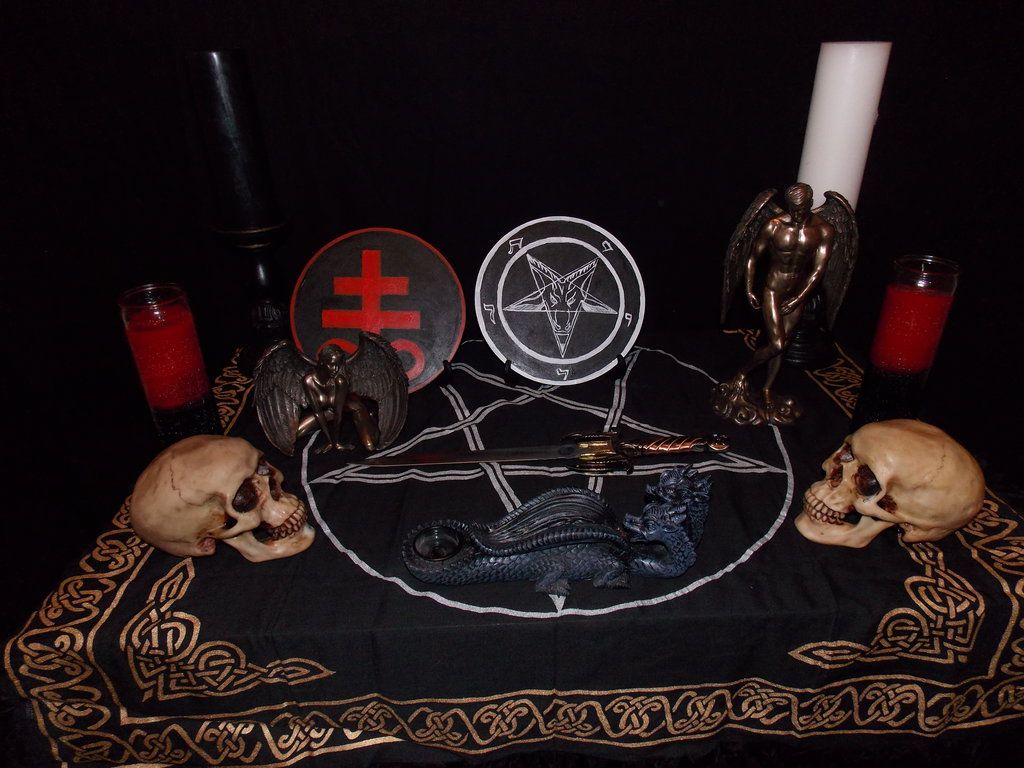

Conclusion
Understanding Satanic rituals requires a nuanced perspective that transcends the sensationalism perpetuated by popular media. Beneath the surface lies a world rich in symbolism, psychology, and individual empowerment. Satanic rituals are not about summoning demons or engaging in nefarious acts, but rather about embracing one’s autonomy, exploring the depths of the human psyche, and challenging the boundaries of conventional thinking. By peeling back the layers of misconception, we can also uncover the true essence of Satanic Hand Signs – a diverse and multifaceted practice that speaks to the complexities of the human experience.






Pingback: Which Religions Believe In Satan? - Witch symbols
Pingback: The Hidden Language of Satanic Hand Signs - Witch symbols
Pingback: Types of Dark Magic: The Most Mysterious and Dangerous Spells in History - Witch symbols